
The Backbone of Modern AI Search, Recommendation, and Discovery
You've probably noticed the shift: instead of scrolling through ten blue links, you now scan the AI-generated summary at the top of Google or Bing. This is semantic search working in tandem with large language models - but what's happening behind the scenes, and where do embeddings fit into this puzzle?
What Are Embeddings, Really?
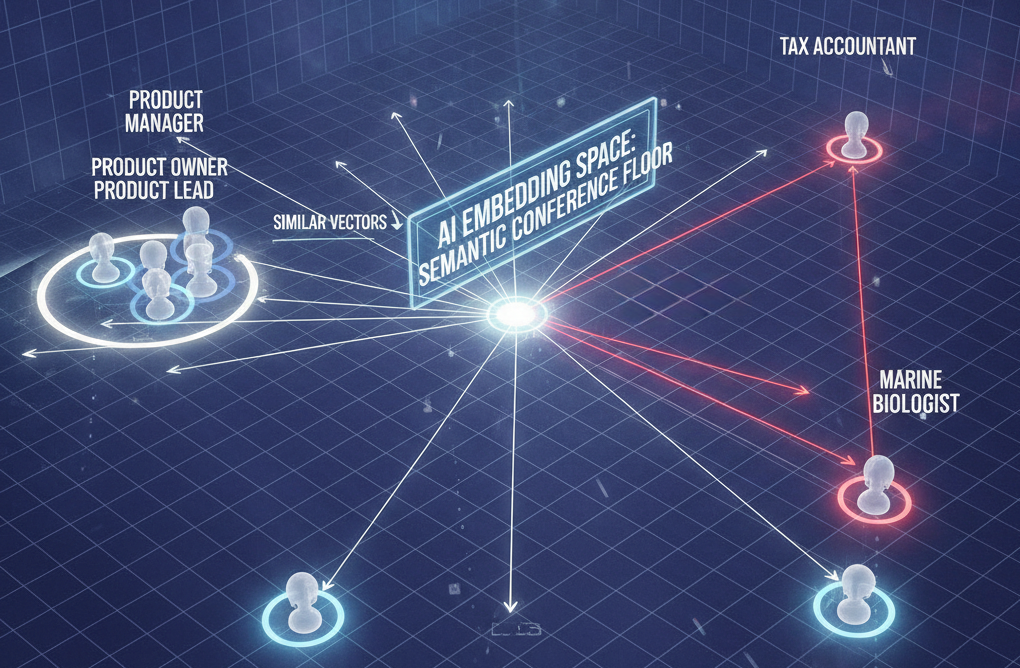
Imagine you're at a massive international conference where thousands of people are mingling, but there are no name tags, no obvious indicators of who does what. How would you find someone who shares your interests, speaks your professional "language," or could help solve a problem you're wrestling with?
Now imagine if everyone had a unique multidimensional coordinate - not marking their physical location, but mapping their expertise, interests, and approach to problem-solving. Suddenly, finding your perfect conversation partner becomes algorithmic: you'd naturally discover people whose coordinates align with yours across dozens of dimensions simultaneously.
This is essentially what embeddings do for AI systems, but instead of mapping people in physical space, they map words, images, products, content - actually any piece of data - in mathematical space based on meaning and relationships. Each of these "coordinates" is known as a vector. Think of a vector as a list of numbers - perhaps [0.2, -0.5, 0.8, ...] - that might be hundreds or thousands of numbers long. Words with similar meanings end up with similar numbers. At our imaginary conference, someone described as "product manager" would have coordinates close to "product owner" and "product lead" in this numerical space, while being far from "tax accountant" or "marine biologist."
This is the breakthrough: unlike traditional search systems that match literal keywords (searching "car" only finds documents containing the word "car"), embeddings understand that "automobile," "vehicle," and "BMW X5" all live in the same semantic neighborhood. They capture context, nuance, and relationships that keyword matching completely misses.
When you search for "cross training sneakers" on a modern e-commerce site, embeddings help the system understand you might also be interested in "trail running shoes" or "offroad trainers" — even if the product descriptions use completely different words. The system doesn't just match text; it matches intent.
This shift from literal matching to meaning-based matching is why your Netflix recommendations have gotten eerily accurate, why Google can answer questions you didn't even finish typing, and why enterprise search finally feels like it actually understands what you're looking for.
The result? AI systems that don't just process data — they comprehend it.
The Three Pillars: Where Embeddings Shine
Embeddings are transforming three core areas of digital experience, each building on that fundamental shift from keyword matching to meaning understanding:
Search: From "Did You Mean?" to "I Know What You Mean"
Traditional search was like having a librarian who could only help if you knew the exact title of the book you wanted. Modern embedding-powered search is like having a librarian who understands the story you're trying to find.
Consider searching for "that movie with the guy who can see dead people." A keyword-based system would struggle, but embeddings connect the dots between your description and "The Sixth Sense" or "Ghost Town," understanding the semantic relationship between your query and movie plot summaries, reviews, and metadata.
In enterprise contexts, this transforms how teams find information. Instead of remembering exact file names or keywords, employees can search for "the presentation about Q3 sales challenges in the Northeast region" and actually find it — even if the document is titled "Regional_Performance_Review_Sept2025.pdf."
Recommendations: Beyond the "Also Bought" Trap
We've all experienced the frustration of recommendation systems stuck in narrow loops—buy one cookbook and suddenly everything suggested is about cooking. Embeddings break free from these silos by understanding deeper patterns and relationships.
Netflix doesn't just know you watched "Stranger Things" - embeddings help it understand you enjoy 80s nostalgia, ensemble casts, supernatural mysteries, and coming-of-age stories. This enables recommendations that might seem surprising but feel eerily perfect: perhaps a Korean thriller with similar emotional beats or a documentary about 80s pop culture.
For B2B platforms, this means recommending not just similar products, but complementary solutions that actually solve related business problems - understanding that someone researching "inventory management software" might also benefit from "demand forecasting tools."
Discovery: Surfacing the Unknown Unknowns
Perhaps the most powerful application is discovery - helping users find valuable content they never knew existed or wouldn't have thought to search for.
LinkedIn's feed doesn't just show you posts from your connections; embeddings help surface content from your broader professional ecosystem that aligns with your interests, career trajectory, and expertise areas. A product manager might discover insights from a UX researcher they've never met, but whose work is semantically relevant to their current challenges.
You can see this idea in action with our own tldr.takara.ai, which uses embeddings to condense and highlight what really matters from long-form articles, surfacing key insights you might have missed. Instead of manually skimming or guessing which sections are relevant, you're guided directly to the most meaningful takeaways - often uncovering connections and ideas beyond what you initially went looking for.

In research and knowledge work, this capability is transformative. Scientific databases can surface related papers across disciplines, legal research platforms can find relevant precedents using different terminology, and content platforms can introduce readers to new topics that expand their interests naturally.
The common thread? All three applications move beyond the limitations of exact matching to understand intent, context, and relationships - creating experiences that feel less like interacting with a database and more like being understood by an intelligent assistant.
The Business Case: Why This Matters Now
The shift to embedding-powered systems isn't just a technological upgrade - it's a competitive necessity that directly impacts the metrics that matter most to business leaders.
Measurable User Experience Improvements
Companies implementing semantic search and recommendations see immediate, quantifiable improvements. E-commerce sites typically report 15-30% increases in search conversion rates when users can find what they're looking for using natural language rather than exact keywords. Customer support teams see dramatic reductions in "no results found" scenarios - often dropping from 20-30% of queries to under 5%.
For enterprise applications, user satisfaction scores consistently improve when systems "understand" intent. Internal enterprise search implementations often see productivity gains measured in hours per employee per week, as teams spend less time hunting for information and more time acting on it.
Revenue Impact Through Better Matching
The financial impact becomes clear when you consider that better matching equals better business outcomes. E-commerce leaders see concrete returns: Amazon attributes 35% of revenue to their recommendation engine. Streaming platforms using embedding-based recommendations see higher viewer retention and increased watch time - Netflix has publicly stated that over 80% of viewer activity comes from their recommendation engine rather than search, demonstrating its central role in user engagement.
For B2B companies, the impact multiplies across the customer journey. Better search helps prospects find relevant solutions faster, reducing sales cycle length. Improved recommendations increase average deal size by surfacing complementary products that actually solve related problems. Post-sale, customers who can easily discover relevant features and content have higher expansion revenue and lower churn rates.
The Competitive Advantage in AI-Driven Markets
Here's the strategic reality: embedding-powered systems create increasingly better experiences as they accumulate more data and user interactions. This creates a compounding advantage that becomes harder for competitors to replicate over time.
Companies that implement these systems early don't just improve current metrics—they begin building the data flywheel that powers future AI capabilities. Every search query, recommendation interaction, and discovery session trains the system to understand their specific users and content better.
The Cost of Standing Still
Perhaps most compelling is the risk of inaction. User expectations are rapidly evolving, shaped by best-in-class experiences from Google, Netflix, and Amazon. B2B buyers increasingly expect the same intuitive, intelligent interfaces in their professional tools that they experience as consumers.
Organizations still relying on keyword-based search and rule-based recommendations aren't just missing opportunities—they're actively frustrating users who know better experiences are possible. In competitive markets, user experience quality often determines which platforms win, regardless of feature completeness.
The question isn't whether to invest in embedding-powered systems, but how quickly you can implement them before the competitive gap becomes insurmountable.
In the second part of our overview of embeddings we'll explore the challenges still posed by this approach.